The Effect of Mosquito Biting Rate on the Malaria Transmission Model using Bifurcation Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24191/jmcs.v8i1.6972Keywords:
Malaria model, stability analysis, bifurcation analysis, transcritical bifurcationAbstract
This paper analyses a simple malaria transmission model to investigate the effect of parameter changes in mosquitoes per capita biting rate on human population, 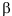 , by using the bifurcation analysis. For further investigation, we first formulated the malaria transmission model into a non-dimensionalized equation. Next, we employed the stability analysis of disease-free equilibrium and endemic equilibrium point of malaria transmission. Using the same non-dimensionalized equation, the one-parameter bifurcation analysis was conducted. A few graphs of the bifurcation diagram, phase plane and time series plot are displayed with the help of mathematical software such as XPPAUT, Maple, and Matlab. Findings reveal that a transcritical bifurcation occurred due to changes in the stability of the system’s equilibrium. When the parameter value of
, by using the bifurcation analysis. For further investigation, we first formulated the malaria transmission model into a non-dimensionalized equation. Next, we employed the stability analysis of disease-free equilibrium and endemic equilibrium point of malaria transmission. Using the same non-dimensionalized equation, the one-parameter bifurcation analysis was conducted. A few graphs of the bifurcation diagram, phase plane and time series plot are displayed with the help of mathematical software such as XPPAUT, Maple, and Matlab. Findings reveal that a transcritical bifurcation occurred due to changes in the stability of the system’s equilibrium. When the parameter value of 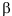 increases, the infected human and infected mosquito population decreases. This finding demonstrates that changes in mosquito biting rates could have an effect on both infected humans and mosquito population.
increases, the infected human and infected mosquito population decreases. This finding demonstrates that changes in mosquito biting rates could have an effect on both infected humans and mosquito population.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Mathematics and Computing Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.







